19. Lecsyony Tseinyabtap: Ati Blaldi xte Tiu Pamyël Nde “This is Not Señor Panfilo’s Blal”

A boundary marker showing the border between two communities in the Tlacolula Valley.
This lesson is about identificational sentences and related patterns. Sections §19.1–19.3 present identificational sentences without “be” and with two “is” verbs, na and rac. Section §19.4 explains more about identificational sentences, and section §19.5 more about rac. Adjectives are introduced in section §19.6.
Ra Dizh
ati [a’ti’] not (negative word used in identificational sentences)
atizh [a’ti’zh] not (negative word used in identificational sentences)
azm [a’zm] asthma
bini [binnih] candle **
bro [bròo’oh] big § mod. ro
bsia [bsihah] eagle
buny Dizhsa [bùunny Dìi’zhsah] Zapotec person
buny Mizh [bùunny Mi’ii’zh] see Mizh
bzhya [bzh:yàa] witch
col [co’oll] line (of people, for instance), queue
caria [carììa’] does not exist
dop [dòo’p] short
gab [ga’ab] few
lasliery [lasliiery] constable
loc [loo’c] crazy
Lia Zyec [Lia Zye’c] Francisca, Chica
Nduny [Nduuny] Antonio
mardom [mardo’mm] mayordomo
Mizh [Mi’ii’zh] / buny Mizh [bùunny Mi’ii’zh] Mixe person
na [nàa] is (irregular verb; see lesson and verb charts)
ncweby [ncwèeby] new § mod. cweby
ncyets [ncye’ts] white
nga [ngàa’ah] green; unripe, raw, uncooked § mod. –ya [ya’ah] (used only for “unripe, raw, uncooked”)
ngas [nga’as] black § mod. –yas [yàa’as] (used only with names of animals and in certain fixed expressions)
ngats [ngaàa’ts] yellow § mod. –yats (used only in certain fixed expressions)
ni rculo zhily [nih rculoh zhi’ìilly] shepherd
ni rguieb lady [nih rguìeb lahdy] tailor
nsual [nsu’all] blue
rac [rahc] 1. is, becomes; 2. happens; 3. hurts, aches; 4. has (an illness) § perf. guc, irr. gac [ga’c], neut. nac [naa’c]
wnya [wnyààa’] traditional healer (curandero, curandera)
xlyia [x:lyiàa’] fever
xlyiayas [x:lyiàa’yàa’as] black fever
xlyiayats [x:lyiàa’yaàa’ts] yellow fever
xnia [xniaa] red
zagru [zagrùu] pretty
zyual [zyuàa’ll] tall
zhi [zhii’ih] cold (illness)
Xiëru Zalo Ra Dizh
-
The main duty of the lasliery or “constable” (alguacil, in Spanish) is to patrol the streets of the community and enforcing curfew. This position, like other municipal offices in San Lucas and other towns in Oaxaca, is a cargo duty (see dialogue VI-4).
-
Diseases are viewed and treated very differently in Zapotec culture from the way we expect in the United States. Your teacher can tell you about diseases like xlyiayas and xlyiayats (not the same as “yellow fever” in Western medicine) and about how diseases are treated by the wnya in a traditional Zapotec community. You can read more about medical vocabulary in section VIII-3 in this unit.
-
As you’ll see in section §19.6.3, some adjectives, such as ncweby, change when used as modifiers. The modifying (“mod.”) form of such adjectives is listed in the Ra Dizh.
§19.1. Identificational sentences without “be”
An IDENTIFICATIONAL sentence tells that one person or thing is the same as another or gives the category to which that person or thing belongs, as with I’m Chica’s brother or The teacher is a woman or This is a blal. In English, we use a form of the verb be to do this. (Be is the most irregular English verb. Forms of be include am, is, are, was, were, and more!) The noun phrase that comes before the form of be in English (I, my teacher, this) is the subject; the noun phrase that comes after the form of be in English (Chica’s brother, the teacher, this) is the PREDICATE, which the speaker uses to identify the subject with.
There are three different ways to express identificational sentences in Valley Zapotec, all of which you have already seen in Blal xte Tiu Pamyël. The simplest one is with the predicate noun phrase followed by the subject, as in the following examples:
|
Bzyan Lia Zyec naa. |
“I’m Chica’s brother.” |
|
Mna mes re. |
“That teacher is a woman.” |
|
Bini nde. |
“This is a candle.” |
|
Buny San Luc Lia Len. |
“Elena is a San Lucas person.” |
|
Ni rculo zhily buny re. |
“That man is a shepherd.” |
Unlike the English sentences, there is no word that means “be” in these sentences! (The other two types of Valley Zapotec identificational sentences do have a word for “be”, as you’ll see later in this lesson.)
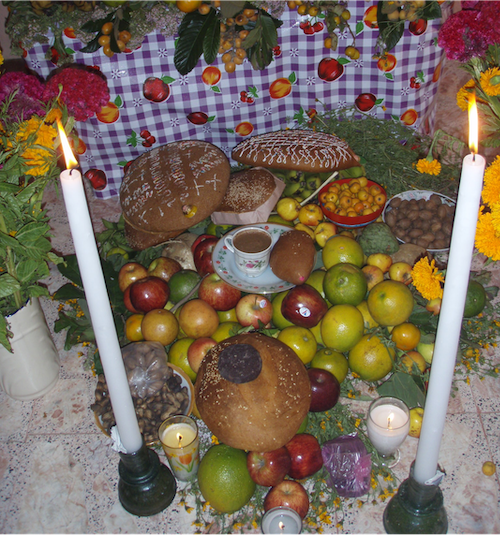
Fot Teiby xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap. Day of the Dead altar in Tlacolula.
This sentence pattern may look very simple, but there is one thing about this pattern that’s quite strange. The subject in the first sentence is expressed not with a bound pronoun, but with a free pronoun!
| predicate (noun phrase) | subject (noun phrase or free pronoun) |
| Bzyan Lia Zyec | naa. |
| Mna | mes re. |
| Bini | nde. |
| Buny San Luc | Lia Len. |
| Ni rculo zhily | buny re. |
This is the first type of Valley Zapotec sentence you’ve seen that uses free pronouns to express subjects. (Maybe free pronouns are used here because there is no verb for the bound pronoun to attach to — but who knows?) As you can see, either the subject or the predicate can be a phrase containing more than one word. Here are some more examples:
|
Mes danoën. |
“We are teachers.” |
|
Doctor yu. |
“You (form.) are a doctor.” |
|
Mniny ni mna loni liu e? |
“Are you the boy I saw?” |
|
Lasliery betsyu e? |
“Is your brother (form.) a constable?” |
You cannot focus the subject in identificational sentences of this type. The predicate always comes first.
Question word identification questions. Here are some examples:
|
Tu laëng? |
“Who is he?” |
|
Tu liu? |
“Who are you?” |
|
Xi liebr re? |
“What is this book?” |
|
Tu buny ren? |
“Who is that man?” |
These questions use the following patterns:
| question word | subject (noun phrase or free pronoun) |
| Tu | laëng? |
| Tu | liu? |
| Xi | liebr re? |
| Tu | buny ren? |
As you can see, it’s the question word that counts as the predicate in this pattern.
Tarea Teiby xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap
Part Teiby. Bcwa ni ca ni guet cuan Dizhsa.
a. That person is Elena’s teacher.
b. Is that woman your doctor?
c. Señora Juana is my friend’s aunt.
d. Are you Chica’s brother?
e. Are you Chico’s brother?
f. This is my dog.
g. Thomas is a city person.
h. They are old people.
i. Is Monica a Mixe person?
j. The shepherd is a Zapotec person.
k. Are you a witch?
l. Are you (form.) a tailor?
m. Who are you (form. pl.)?
n. What is this?
Part Tyop. Give a positive response to each of the following Zapotec questions, using a complete sentence beginning with a “yes”.
a. Mes xtenu naa e?
b. Xamiegwa liu e?
c. Doctor yuad e?
d. Buny Dizhsa Dad Chiecw e?
e. Ra mna ni gucne mniny re laad e?
f. Bxady nde e?
g. Buny Bac betsu e?
h. Studian laad e?
i. Bxuaz pryema e?
Negative versions of this type of identificational sentence do not use queity. Instead, they use a new identificational negative word, ati [a’ti’]. Here are some examples:
|
Ati mnadi mes re. |
“That teacher is not a woman.” |
|
Ati mesdi mna re. |
“That woman is not a teacher.” |
|
Ati blaldi nde. |
“This is not a blal.” |
|
Ati mesdi danoën. |
“We are not teachers.” |
|
Ati ni rculo zhilydi larëng. |
“They are not shepherds.” |
The negative ending –di is used following the predicates in these sentences, just as –di follows the verb in sentences with the regular negative word queity. However, when the predicate consists of a possessed noun phrase like bzyan Bed or xabal Tiu Pamyël, -di goes immediately after the possessed noun, rather than at the end of the possessed noun phrase:
|
Ati bzyandi Lia Zyec naa. |
“I am not Chica’s brother.” |
|
Ati xablaldi Tiu Pamyël nde. |
“This is not Señor Panfilo’s blal.” |
|
Ati blaldi xte Tiu Pamyël nde. |
“This is not Señor Panfilo’s blal.” |
|
Ati xnandya liu. |
“You aren’t my mother. |
The pattern for negative sentences where the predicate is not possessed is:
| ati | predicate | -di | subject |
| Ati | mna | -di | mes re. |
| Ati | mes | -di | mna re. |
| Ati | blal | -di | nde. |
| Ati | mes | -di | danon. |
| Ati | ni rculo zhily | -di | larëng. |
The pattern for negative sentences whose predicates are possessed is:
| ati | possessed noun (predicate) | -di | possessor | subject |
| Ati | bzyan | -di | Bed | naa. |
| Ati | xablal | -di | Tiu Pamyël | nde. |
| Ati | blal | -di | xte Tiu Pamyël | nde. |
| Ati | xnan | -di | -a | liu. |
In these sentences, the negative particle –di comes right after the possessed noun, followed by the possessor and the subject. If xte or xten is used, this word comes before the possessor, after –di. Since it is the possessed noun that is the actual predicate, the basic pattern is the same (it just may seem a little unexpected!).
Something similar happens with the “must” particle –zhyi. If the predicate is not possessed, as in the first example below, –zhyi follows the predicate. When the predicate is possessed, as in the second example, –zhyi comes right after the possessed noun (which, again, is the actual predicate).
|
Blalzhyi nde. |
“This must be a blal.” |
|
Xablalzhyi Tiu Pamyël nde. |
“This must be Señor Panfilo’s blal.” |
In all these examples, then, –di and –zhyi go right after the first word of the predicate (before any other endings, such as possessor endings). This is the pattern you will hear in most cases. Listen to how Valley Zapotec speakers construct identificational sentences without “be”, and you may hear other sentence patterns, however.
Don’t try to use the patterns in this section if the subject of the sentence is a plural noun phrase containing ra or two nouns joined by cuan “and” — speakers feel these sentences don’t sound appropriate. You’ll learn about identificational sentences with plural subjects in the next section.
Tarea Tyop xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. First, read the following Zapotec sentences out loud. Chiru bcwa ni ca ni guet cuan Ingles.
a. Buny Bac Bed.
b. Doctor xtenyuad Lia Zhuan.
c. Xamiegwu Mazh.
d. Buny Dizhsa lang.
e. Wnya mna re.
f. Lasliery xtada.
g. Mes xbieda.
h. Cosiner xamiegw Rnest.
i. Bets Lieb lai.
j. Gyizh ni rguieb lady.
Part Tyop. Make each of the sentences in Part Teiby negative, paying special attention to the placement of –di. Translate your new sentences into English.
Part Chon. Change each of the sentences in Part Teiby so that they use the “must” particle –zhyi. Translate your new sentences into English.
Part Tap. Answer the following questions in Zapotec. If the answer is negative, give a positive sentence that identifies the picture, as in the example.
Example: Manyser nde e?
Answer: Yac, ati manyserdi nde. Bdua nde.
a. Xyecwu nde e?
b. Guan nde e?
c. Gyag nde e?
d. Cabai nde e?

e. Mansan nde e?

f. Blal nde e?

g. Caj nde e?

h. Yu nde e?

§19.2. Identificational sentences with na
Using na to say “is” or “are”. The second type of Valley Zapotec identificational sentence uses the word na [nàa], a “be” verb which usually can be translated with “is” or “are”. (Listen to your teacher! Na “is” is not pronounced the same as the words na “now” or na “says”, or as naa “I”. Can you pronounce all these words so that another student can identify which one you mean?) Here are some examples:
|
Cwen re na cwen xten Lia Len cuan Bed. |
“This story is the story of Elena and Pedro.” |
|
Chiecw na xtad Lia Len cuan Bed. |
“Chico is Elena and Pedro’s father.” |
|
Buny San Luc na Bed. |
“Pedro is a San Lucas person.” |
|
Interpol na polisia internasyonal. |
“Interpol is the international police force.” |
|
Doctor na Rnest. |
“Ernesto is a doctor.” |
|
Elena Morales na la Lia Len cuan Dizhtily o cuan Ingles.” |
“Lia Len’s name is Elena Morales in Spanish or English.” |
These sentences are translated in the present, and that is generally how we will translate na in this book, but you may hear speakers use na to refer to the past as well. In that case, it may be translated “was” or “were”. You can suggest this by using the adverb chicy “then, at that time”, as in:
|
Doctor na Rnest chicy. |
“Ernesto was a doctor then.” |
As you can see, these sentences look quite similar to the first type of identificational sentence, but they have na between the subject and the predicate. There is a difference, however. This na pattern has two versions, one with the predicate first, one with the subject first:
| predicate | na | subject noun phrase |
| Buny san Luc | na | Bed. |
| Doctor | na | Rnest. |
| Elena Morales | na | la Lia Len. |
| Xtad Lia Len cuan Bed | na | Chiecw. |
| subject noun phrase | na | predicate |
| Cwen re | na | cwen xte Lia Len cuan Bed. |
| Chiecw | na | xtad Lia Len cuan Bed. |
| Interpol | na | polisia internasyonal. |
| Rnest | na | doctor. |
Both types of sentences are used frequently, and speakers feel that there is little difference in meaning between them. (As you can see, you can often say the same sentence both ways.) The subject-first pattern is especially common when the predicate is a long phrase.
(You may wonder how you can tell the difference between subject and predicate. The subject is the person or thing you are talking about and trying to identify for your hearer; the predicate is what you are using to identify that person. Sometimes, of course, it might be possible to view a sentence both ways!)
Using teiby in the predicate. A predicate in an identificational sentence with na may contain teiby “a”:
|
Teiby doctor na Rnest. |
“Ernesto is a doctor.” |
|
Bsia na teiby many. |
“An eagle is a bird.” (or “The eagle is a bird.”) |
In the English translations of such sentences, a appears before the noun in the predicate (a doctor, a bird, and so on). In Valley Zapotec predicates, teiby is equivalent to English a – but it is not always used — speakers feel that sentences like Doctor na Rnest and Teiby doctor na Rnest mean just the same. (Teiby is not used in identificational sentences without a “be” word.)
Identificational sentences with plural subjects. Here are some identificational sentences with plural subjects:
|
Doctor na ra mna. |
“The women are doctors.” |
|
Mes na Jwany cuan Bed. |
“Juan and Pedro are teachers.” |
In sentences like these, the predicate usually comes first. Speakers feel that if the subject is first, it is focused, and sounds very emphatic:
|
Ra mna na doctor. |
“The women are doctors.” |
Even though we use doctors in the English predicate, ra is never used in the predicate of a Zapotec identificational sentence. A sentence like <Ra doctor na ra mna> doesn’t sound like good Zapotec.
Negative sentences with na. Negative identificational sentences with na work similarly to negative identificational sentences without “be”:
|
Ati doctordi na Rnest. |
“Ernesto is not a doctor.” |
|
Ati mesdi na ra mna re. |
“Those women are not teachers.” |
Again, the sentence starts with the special identificational negative word ati, with –di after the predicate, followed by na and the subject.
| ati | predicate | -di | na | subject |
| Ati | doctor | -di | na | Rnest. |
| Ati | mes | -di | na | ra mna re. |
If the predicate is a possessed noun, the possessor comes between the predicate plus –di and na, just as in the first type of negative identificational sentence:
|
Ati xablaldi Tiu Pamyël na nde. |
“This is not Señor Panfilo’s blal.” |
|
Ati blaldi xte Tiu Pamyël na nde. |
“This is not Señor Panfilo’s blal.” |
Tarea Chon xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Make up new identificational sentences in Zapotec using the following subjects and na.
a. Nduny
b. ra buny
c. mes xte Mazh
d. xtada
e. bets Lia Zyec
f. teiby manyser
g. meser re
h. polisia
i. pristen
j. nde
Part Tyop. Take each of the sentences you wrote in Part Teiby and change it to an identificational sentence without “be”, if you can. If it is not an identificational sentence that can be expressed without “be”, than say so.
Part Chon. Work with a partner. Student A should read a few of his or her sentences from Part Teiby or Part Tyop to Student B. Student B should write down the sentences and then check to see that they’re right. When you’re done, switch roles!
Na with pronoun subjects. Here are some examples of na used with pronoun subjects:
|
Teiby doctor naëb., Doctor naëb. |
“He’s a doctor.” |
|
Lang naëng mniny. |
“He is a child.” |
|
Mes naën. |
“We are teachers.” |
|
Buny Dizhsa narëng. |
“They are Zapotecs.” |
As you would expect, a pronoun subject is expressed with a bound pronoun attached to na. As the examples show, several patterns are possible. Most commonly, the predicate comes first in the sentence, followed by na and the bound pronoun subject:
| predicate | na | bound pronoun subject |
| Teiby doctor | na | -ëb |
| Doctor | na | –ëng |
| Mes | na | -ën |
| Buny Dizhsa | na | -rëng |
Alternatively, you can focus the subject pronoun. In this case, the focused pronoun subject comes first, followed by na, the bound pronoun subject, and the predicate:
| free pronoun | na | bound pronoun subject | predicate |
| Laëng | na | -ëng | mniny. |
Here are the forms of na with attached bound pronoun subjects:
|
nayu [nàayuu’] “you (formal singular) are” naëng [nàa’-ëng] “he (proximate) is” nai [nài’] “he (distal) is” naëb [nàa-ëhb] “he (respectful) is” naëm [nàa’-ëhmm] “he (animal) is” naazh [nàa-ahzh:] “he (familiar) is” naën [nàa-ëhnn] “we are” naad [nàa-ahd] “you (informal plural) are” nayuad [nàayùad] “you (formal plural) are” narëng [nàarëng] “they (proximate) are” nari [nàarih] “they (distal) are” narëb [nàarëhb] “they (respectful) are” narëm [nàarëhmm] “they (animal) are” narazh [nàarahzh:] “they (familiar) are” |
Na is never used with “I” or informal “you” singular subjects. (No one knows why! But if you want to make an identificational sentence with an “I” or informal “you” subject, you can express it without “be”, as in section §19.1, or with another pattern you’ll learn later in this lesson.)
Negative na sentences with pronoun subjects are quite similar to other negative na sentences:
|
Ati doctordi naëb. |
“They are not doctors.” |
|
Ati ni rguiby ladydi naën. |
“We are not tailors.” |
|
Ati Buny Dizhsadi narëng. |
“They are not Zapotecs.” |
As you can see, the pattern is the same as the one you saw earlier:
| ati | predicate | -di | na | subject (noun phrase or bound pronoun) |
| Ati | doctor | -di | na | Rnest. |
| Ati | mes | -di | na | ra mna re. |
| Ati | doctor | -di | na | -ëb. |
| Ati | mes | -di | na | -ën. |
| Ati | Buny Dizhsa | -di | na | -rëng. |
Question word questions with na. Here are some examples of question word questions with na:
|
Tu naëng? |
“Who is he?” |
|
Xi na liebr re? |
“What is this book?” |
|
Tu na buny ren? |
“Who is that man?” |
These questions use the following patterns:
| question word | na | subject (noun phrase or bound pronoun) |
| Tu | na | ëng? |
| Xi | na | liebr re? |
| Tu | na | buny ren? |
There may be a subtle difference in meaning between these questions and those without na. See what your teacher thinks.
Tarea Tap xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Bcwa ni ca ni guet cuan Dizhsa.
a. We are your friends.
b. I am a Zapotec person.
c. He (prox.) is a Mixe person.
d. She (resp.) must be a constable.
e. He (fam.) isn’t a priest.
f. Those are bulls.
g. You guys must be Ignacio’s brothers.
h. He (dist.) isn’t my father.
i. They (resp.) are Leon’s teachers.
j. They (prox.) are witches.
Part Tyop. Sentence (a) in Part Teiby could answer a question like Laad xamiegwën e? or Tu naad?. For each of your other Zapotec sentences in Part Teiby, create a mini-dialogue by making up an appropriate question. Use some a-queity questions and some question word questions. Practice your question-and-answer pairs with another student.
Part Chon. Now convert each of the sentences you wrote in Part Teiby to an identificational sentence without “be”, if possible. If the sentence cannot be expressed without “be”, say so.
Asking someone’s name. Here’s a very important type of identificational question that usually doesn’t use na or nac:
|
Tu loo? |
“What’s your name?” |
|
Tu layu? |
“What’s your (form.) name?” |
|
Tu la mna re? |
“What is that woman’s name?” |
Asking someone’s name uses an identificational question without “be”. What may seem odd here is that in English we say this with “what”, but in Zapotec you use the word “who”!
More about na. Na looks like a neutral verb — it refers to a state, and it begins with n. But unlike the neutral verbs you learned about in Lecsyony Tseinyabchon, there are no other forms of this verb. Na only is used in this one form — it has no habitual, perfective, or irrealis stem (or any other form at all).
§19.3. Identificational sentences with forms of rac
Rac: another way to express “be”. The third type of Valley Zapotec identificational sentence uses a “be” verb that works much more like an ordinary verb. Rac [rahc] “is” has a habitual, a perfective guc [guhc], and an irrealis gac [ga’c], as well as a neutral nac [naa’c]. (In identificational sentences, all these other forms are more common than the habitual rac.) Here are some examples of identificational sentences with forms of rac.
|
Doctor gac Nduny. |
“Antonio is going to be a doctor.” |
|
Wnya guc mna re. |
“That woman used to be a healer.” |
|
Mardom naquëb. |
“He (resp.) is a mayordomo.” |
|
Daru chu zhi gacrëng studian xte unibersida. |
“Someday they will be college students.” |
|
Tu nacu? |
“Who are you?” |
When it’s important to specify a past or future time for an identificational sentence, you should use a form of rac. Note, though, that the perfective often suggests that the person you are talking about is no longer alive — so when you say Mes guc mna re, “that woman” is probably dead.
Most forms of rac with bound pronoun subjects are completely regular in their pronunciation and spelling. Here are the forms you need to pay attention to:
|
raca [ràa’ca’] “I am” racu [ràa’cùu’] “you are” raquëng [rahquëng] “he (prox.) is” raqui [rahquih] “he (dist.) is” raquëb [rahquëhb] “he (resp.) is” raquëm [rahquëhmm] “he (anim.) is” raquën [rahquëhnn] “we are” |
(Remember, c becomes qu before ë or i.) The other tenses work in a similar way. As you know, you can check the forms of any verb in the verb charts at the end of this book.
The examples above follow a pattern very similar to those of the identificational sentences you have seen before:
| predicate | form of rac | subject |
| Doctor | gac | Nduny. |
| Mes | guc | mna re. |
| Mardom | naqu | -ëb. |
| Tu | nac | -u? |

Fot Tyop xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap. What’s written here? Who should wear this shirt?
If you want to use the particle –zhyi with an identificational sentence containing nac or another form of rac, it goes on the predicate:
|
Bzhyazhyi nacëng. |
“She must be a witch.” |
Putting the subject first in an identificational sentence with nac shows a strong focus:
|
Nduny nac doctor. |
“Antonio is a doctor.” |
Habitual rac often has the meaning of “becomes” or “gets to be”, as in
|
Gab buny rac doctor. |
“Few people become doctors.” |
(Gab [ga’ab] means “few”.) The same translation is often used for the irrealis:
|
Doctor gac Nduny. |
“Antonio is going to be a doctor.”, “Antonio is going to become a doctor.” |
Negative sentences with rac. Negative identificational sentences with rac follow a pattern that is similar to the other negative identificational patterns. Here are some examples, and the new pattern:
| Ati doctordi nac Nduny. | “Antonio isn’t a doctor.” |
| Ati doctordi gaquëng. | “He won’t become a doctor.” |
| Ati mesdi guc mna re. | “The woman wasn’t a teacher.” |
| Ati mardomdi naquëb. | “He’s not a mayordomo.” |
| ati | predicate | -di | form of rac | subject |
| Ati | doctor | -di | nac | Nduny. |
| Ati | doctor | -di | gac | -ëng. |
| Ati | mes | -di | guc | mna re. |
| Ati | mardom | -di | nac | -ëb. |
Tarea Gai xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Bcwa ni ca ni guet cuan Ingles.
a. Teiby budy naquëm.
b. Ati doctordi guc xnana.
c. Cosiner nacu e?
d. Mes rac Lia Zhuan.
e. Betsëng gac mardom.
f. Bxuazzhyi naquëb.
g. Ati xamiegwdya nac meser re.
h. Lia Petr guc mna re.
i. Chiecw nac pristen.
j. Rregal nac ra gyia re.
Part Tyop. Change the tense of each of the sentences above to make additional sentences, using neutral, irrealis, perfective, or perhaps habitual forms of rac. What do your new sentences mean?
§19.4. More about identificational sentences
A-queity questions with na and rac. If you want to question an identificational sentence that uses na or a form of rac, you can simply add e at the end of the pattern with the predicate first, followed by na or a form of rac, followed by the subject.
|
Doctor na Nduny e? |
“Is Antonio a doctor?” |
|
Bxuaz cayac Bed e? |
“Is Pedro becoming a priest? |
Starting the question with the subject puts focus on the subject:
|
Ra mna na mes e? |
“Are the women teachers?” |
|
Chiecw nac xtad Lia Len e? |
“Is Chico Elena’s father?” |
Some questions use another word order that’s not usually used in simple identificational sentences like those you saw in sections §19.2–§19.3, as in
|
Na Nduny doctor e? |
“Is Antonio a doctor?” |
|
Nac Chiecw xtad Lia Len e? |
“Is Chico Elena’s father?” |
This word order, with the “be” word first, followed by the subject, and then the predicate, can be used in questions and also in more complicated sentences, such as
|
Ria buny scwel chi na buny mniny. |
“A person goes to school when a person is a child.”, “One goes to school when one is a child.” |
(Buny “person” is frequently used in sentences like this, where the speaker wants to make a general statement about people in general.)
Negative sentences with atizh. In sections §19.1–§19.3, you learned to use ati to make identificational sentences negative. There is another way to make identificational sentences (both with and without “be”) negative, by using a different identificational negative word, atizh [a’ti’zh:], rather than ati. Sentences with atizh usually don’t use –di:
|
Atizh doctor Rnest. |
“Ernesto is not a doctor.” |
|
Atizh mes na ra mna re. |
“The women are not teachers.” |
(You will hear some speakers use –di in these sentences. In that case, atizh works just like ati.)
Tarea Xop xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Change the following sentences into questions.
a. Teiby becw naquëm.
b. Gyizh rac Lia Desy.
c. Betsëng gac studian.
d. Bzhyazhyi naquëb.
e. Tan nac mardom.
f. Rregal nac bistied.
Part Tyop. Change the following sentences so that they use the verb na.
a. Teiby guan naquëm.
b. Meszhyi naquëb.
c. Ati xamiegwdya nac doctor re.
d. Chiecw nac buny Mizh.
e. Rregal nac ra liebr re.
Part Chon. Change the following sentences so that they don’t use a “be” word.
a. Teiby zhyet naquëm.
b. Pristenzhyi naquëb.
c. Ati xamiegwdya nac mardom.
d. Chiecw nac mes.
e. Rregal nac zhimy.
Part Tap. Change the following sentences so that they use atizh instead of ati.
a. Ati doctordi guc xnana.
b. Ati xamiegwdya nac studien.
c. Ati pristendi gaquëng.
d. Ati mesdi guc mna re.
e. Ati wnyady naquëb.
Identification and location. In English, identificational sentences like Ernesto is a doctor and locational sentences like Ernesto is in the museum seem quite similar, because they both use the verb is. These two types of sentences are very different in Zapotec. Unlike identificational sentences, Zapotec locational sentences need to have a verb. The identificational verbs na and rac that you’ve learned in this lesson are generally not used in locational sentences, and locational verbs are generally not used in identificational sentences in Zapotec. (You will learn about one type of locational sentence that uses na in Lecsyony Galy.)
§19.5. More about rac
Rac has a number of other meanings and uses. Some of these may seem similar to the “be” idea, but others may not! These other types of rac sentences are not identificational, however, so they do not contain noun predicates, and they don’t use ati or atizh for their negatives.
“Happens”. First, rac can also mean “happens”, as in
|
Los Angl guqui. |
“It happened in Los Angeles.” |
|
Xi cayac? |
“What is happening?” |
(The progressive of rac, cayac [cayahc], makes sense with this meaning of the verb, but not in its identificational use.) In these sentences, the subjects are the bound pronoun –i “it” and xi “what”. Sometimes, however, you will see rac used without a subject, to mean “it happens” with nothing used to say “it”, as in
|
Xa guc? |
“How did it happen?” |
Sentences about illness. Two additional meanings of rac that are related to illness. Rac can mean “hurts” or “aches”, as in
|
Rac nia. |
“My foot hurts.” |
|
Guc guecy Lia Petr e? |
“Did Petra’s head ache?” |
In these examples, the body part that hurts is the subject of rac. With a person as the subject, rac can mean “suffers from” or “has (an illness)”:
|
Raquëng zhi. |
“He has a cold.” |
|
Raca azm. |
“I have asthma.” |
|
Rac xnana xlyiayats. |
“My mother has yellow fever.” |
You’ll learn more about ways to talk about illness in S-23 at the end of this unit.
Negatives of the new rac sentences. To make a sentence with one of these new uses of rac negative, use queity, not ati or atizh.
|
Queity gucdyi Los Angl. |
“It didn’t happen in Los Angeles.” |
|
Queity racdi nia. |
“My foot doesn’t hurt.” |
|
Queity gucdi guecy Lia Petr. |
“Petra didn’t have a headache.” |
Ati and atizh are only used in negatives of identificational sentences. When rac means “happens” or “hurts”, it’s working more like a normal verb, not as an identificational “be”.
“Exists”. Finally, rac can mean “exists”, as in
|
Rac col. |
“There’s a line.”, “A line exists.” (This might be used to tell someone he ought to get into the line of people waiting!) |
English translations of sentences like this will often use “there is” or “there are”.
To make an “exists” sentence negative, you use a special negative verb, caria [carììa’] “does not exist”. This verb goes at the beginning of the sentence, but does not need a –di:
|
Caria col. |
“There’s no line.”, “The line does not exist.” |
Tarea Gaz xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Bwca ni ca ni guet cuan Dizhsa.
a. What happened in Oaxaca?
b. Does your stomach hurt?
c. Ignacio doesn’t have asthma.
d. The dog’s foot doesn’t hurt.
e. Is there a line?
f. How will it happen?
g. Tomas’s head hurts.
h. My brother has a cold.
i. There is no money.
j. There is homework.
§19.6. Adjectives
An ADJECTIVE is a word like English blue, old, tall, or new — usually, adjectives name qualities that can be used to describe things. Adjectives are used in two main ways. First, they can be predicates, as in English sentences like This book is blue or Jeronimo’s car is new (blue and new here are called PREDICATE ADJECTIVES). Alternatively, they can be used as MODIFIERS of nouns, in noun phrases like blue book and new car (in these noun phrases, blue and new are MODIFYING ADJECTIVES). A modifier is a single word that works similarly to the modifying phrases you learned about in Lecsyony Tseiny (15), by telling some characteristic of a noun that the speaker wants to mention.
In Valley Zapotec, many adjective ideas are expressed with verbs. Some examples you’ve already learned include rcyetlaz “gets happy, is happy”, rdyan “gets hungry”, rzhiby “gets scared”, and ryac “gets well”. (Habitual forms of Valley Zapotec verbs that express adjective ideas usually include the meaning “gets”.)
Valley Zapotec also has adjectives that are not verbs. Here are some examples:
|
bro [bròo’oh] big dop [dòo’p] short loc [loo’c] crazy ncweby [ncwèeby] new ncyets [ncye’ts] white nga [ngàa’ah] green ngas [nga’as] black ngats [ngaàa’ts] yellow nsual [nsu’all] blue xnia [xniaa] red zagru [zagrùu] pretty zyual [zyuàa’ll] tall |
(As you can see, many Valley Zapotec adjectives start with n.) As in English, these adjectives can be both predicates and modifiers.
Predicate adjectives. Valley Zapotec sentences with predicate adjectives and noun subjects look like identificational sentences. Here are some examples:
|
Ncyets na yu. |
“The house is white.” |
|
Ncyets nac yu. |
|
|
Ncyets yu. |
|
|
Nsual na liebr. |
“The book is blue.” |
|
Nsual nac liebr. |
|
|
Nsual liebr. |
|
|
Ncweby na xcarr Rony. |
“Jeronimo’s car is new.” |
|
Ncweby nac xcarr Rony. |
|
|
Ncweby xcarr Rony. |
These three groups of sentences illustrate patterns for predicate adjectives that are just like the three basic patterns you learned for identificational sentences: first comes the predicate adjective; next either na, a form of rac, or no “be”; and finally the subject.
However, things are a little different with pronoun subjects. The na and nac patterns look just like the identificational sentences, but a different pattern is used for the third type of sentence, the one that doesn’t use a “be” verb:
|
Ncyets nang. |
“It’s white.” |
|
Ncyets naquëng. |
|
|
Ncyetsëng. |
|
|
Ncweby nai. |
“It’s new.” |
|
Ncweby naqui. |
|
|
Ncwebyi. |
Here’s the pattern:
| adjective predicate | subject (noun phrase or bound pronoun) |
| Ncyets | yu. |
| Ncyets | -ëng. |
| Ncweby | xcarr Rony. |
| Ncweby | -i. |
As the examples show, when you don’t use a “be” verb, subjects of adjective predicates are shown by bound pronouns (not by free pronouns, as in identificational sentences).
Although each of the ten new adjectives in this lesson can be used in all three of these patterns (with na, with a form of rac, and without “be”), many other Valley Zapotec adjectives sound best to speakers only in one or two of these ways (only with na, only with a form of rac, or only with no “be” verb). You’ll learn more about using different types of predicate adjectives by listening to people talking the language.
Another predicate adjective pattern (for adjectives that can be used with na) is for the subject to come first, followed by na, and then the predicate adjective.
|
Yu na ncyets. |
“The house is white.” |
|
Liebr na nsual. |
“The book is blue.” |
|
Xcarr Rony na ncweby. |
“Jeronimo’s car is new.” |
This subject-first pattern is usually only with a noun subject plus na, not with forms of rac or without a “be” verb.
Tarea Xon xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Make up a new Zapotec sentence using each of the following adjectives. Be sure to try out all three patterns: with na, with rac, and with no “be”.
a. dop
b. loc
c. ncweby
d. bro
e. nga
f. ngas
g. ngats
h. nsual
i. xnia
j. zyual
k. zagru
Part Tyop. Work with a partner, and take turns reading your sentences out loud to each other. When listening to your partner’s sentence write it down and translate it into English. Then check with your partner to see if you got it right!
As with identificational sentences, negative predicate adjective sentences use ati or atizh rather than queity.
|
Ati ncyetsdi na liebr. |
“The book isn’t white.” |
|
Ati ncyetsdi nac liebr. |
|
|
Ati ncyetsdi liebr. |
|
|
Ati ncyetsdi nang. |
“It isn’t white.” |
|
Ati ncyetsdi naquëng. |
|
|
Ati ncyetsdyëng. |
Speakers may feel that negative sentences with no “be” verb (the last pattern in each set) seem contrastive (suggesting something like “…rather, it’s red”).
As you know, atizh sentences are also contrastive.
|
Atizh ncyets na liebr. |
|
Atizh ncyets nac liebr. |
|
Atizh ncyets liebr. |
To make a question from a predicate adjective sentence, just put e at the end of a sentence beginning with the predicate adjective:
|
Ncweby na xcarr Rony e? |
“Is Jeronimo’s car new?” |
|
Ncweby nac xcarr Rony e? |
|
|
Ncweby xcarr Rony e? |
|
|
Ncweby nai e? |
“Is it new?” |
|
Ncweby naqui e? |
|
|
Ncwebyi e? |
Tarea Ga xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Make up negative sentences with predicate adjectives describing the pictures below. Be creative!
a. 
b. 
c. 
d. 
Part Tyop. Make questions with predicate adjectives about the following items. Then see if a fellow student can answer your questions with complete sentences.
a. 
b. 
c. 
d. 
Modifying adjectives. Here are some sentences containing modifying adjectives:
|
Mna bini ncyets. |
“I saw the white candle.” |
|
Bdeidy mes Bed liebr nsual. |
“The teacher gave Pedro the blue book.” |
|
Lany caj ngas nuëng. |
“It’s in the black box.” |
|
Doctor na mna zagru. |
“The pretty woman is a doctor.” |
|
Bzi Rony teiby carr cweby. |
“Jeronimo bought a new car.” |
|
Zubëng lany ydo ro. |
“He’s sitting in the big church.” |
These sentences illustrate the Valley Zapotec modifying adjective pattern:
| noun | modifyng adjective |
| bini | ncyets |
| liebr | nsual |
| caj | ngas |
| mna | zagru |
| carr | cweby |
| ydo | ro |
In Valley Zapotec, modifying adjectives come after the nouns that they modify (just as with the modifying phrases you learned about in Lecsyony Tseiny (15)). This is different from English, where modifying adjectives come before the noun. (Some Valley Zapotec modifiers, such as numbers and words like gab “few”, do come before the noun.)
If you look at the last two examples, you can see something extra that happens with some modifying adjectives. Certain adjectives that start with n when used as predicates lose this n when used as modifiers. The modifying form of ncweby “new” is cweby — so we say Ncweby carr “The car is new”, but carr cweby “new car”. There are other patterns too. The modifying form of bro “big” is ro. Every adjective that changes when used as a modifier (“mod.”) will have this listed in its Ra Dizh and Rata Ra Dizh entries.
Special modifier forms of color adjectives. A few adjectives referring to color have special modifer forms that are used only in certain types of words.
-
Ngas “black” has the special modifying form –yas [yàa’as]. This special modifier form of ngas is not a separate word, but is added as an ending on the noun it follows. It’s used only with words for black animals (such as becwyas [bèe’ecwyàa’as] “black dog”) and in a few other fixed expressions (such as xlyiayas [x:lyiàa’yàa’as] “black fever”). When modifying other nouns, however, ngas does not change.
-
Nga “green; unripe” works in two different ways, depending on meaning. When it refers only to color, the modifying form is unchanged (ngas). When it means “unripe, raw, uncooked”, the modifying form is –ya [ya’ah], as in nrazhya “unripe orange”. This modifying form is also an ending.
-
Ngats “yellow” has a special modifying ending form –yats [yaàa’ts] that is used primarily in fixed expressions, such as xlyiayats [x:lyiàa’yaàa’ts] “yellow fever”. You don’t really need to memorize this modifying form, since you can’t use it to make up new expressions yourself, but it’s good to be able to recognize it when you hear it.
Other color adjectives work like normal modifying adjectives.
Tarea Tsë xte Lecsyony Tseinyabtap.
Part Teiby. Bcwa ni ca ni guet cuan Dizhsa.
a. My mother is a short woman.
b. Juan is not a crazy city person.
c. Give me a new pencil!
d. Petra bought a pretty dress.
e. Is Soledad’s husband a tall man?
f. The green bag is missing.
g. Why is the black dog barking?
h. Tomas asked for a red apple.
i. Chica wants a blue car and a big house.
j. Catalina likes yellow flowers.
k. That is an unripe peach.
l. Who took your black book?
Part Tyop. First, identify the noun phrases containing modifying adjectives in each of the Zapotec sentences you wrote for Part Teiby. Then, make up new sentences based on these phrases that use the adjectives as predicates, as in the example below (for sentence j). Try to use all three different predicate adjective sentence patterns in your answers.
Example (j). The noun phrase containing a modifying adjective is gyia ngats.
Answer. Ngats gyia. “The flower is yellow.”
Part Chon. ** Bcwa cuan Dizhsa! You’ve learned a lot about how to describe people and things in this lesson. Write a short paragraph describing some of the things you see in Fot Teiby at the beginning of this lesson. Do the best with the vocabulary you have, and remember you can use positive sentences, negative sentences, and even the location sentences that you learned about earlier. Sometimes you won’t know all the words you would like to use, but do your best and ask your teacher if you need help. Be creative and have fun!
Abbreviations
mod. modifying, modifier
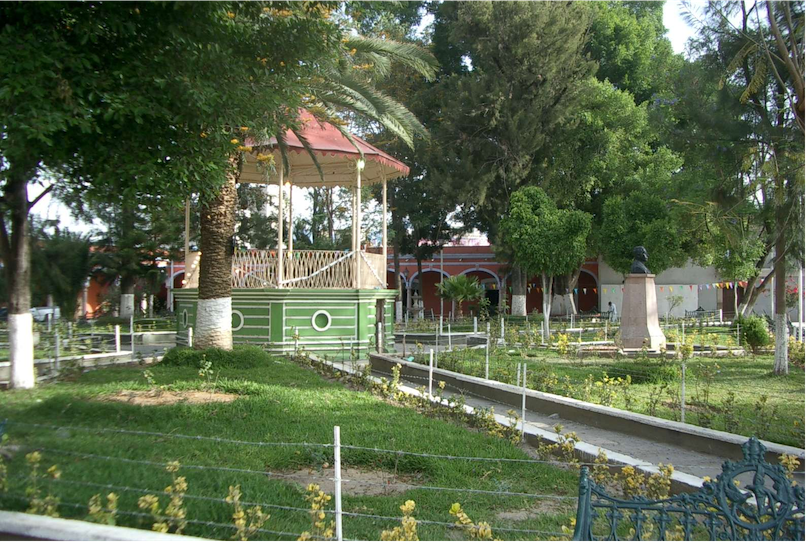 Fot Chon. The gazebo in the center of the jardín (central square) in Tlacolula.
Fot Chon. The gazebo in the center of the jardín (central square) in Tlacolula.
A SENTENCE that tells that one person or thing is the same as another or that gives the category something belongs to. The following are identificational sentences: I am a teacher; that person is a waiter.
In an IDENTIFICATIONAL SENTENCE, the part of the SENTENCE that the speaker is using to identify the SUBJECT. In the sentence Juan is a doctor, doctor is the predicate.
A word used to name a quality. English examples include silly, red, and beautiful. See also MODIFYING ADJECTIVE, PREDICATE ADJECTIVE.
An ADJECTIVE that is used a PREDICATE, such as blue in This book is blue.
A word used to tell a characteristic of a NOUN or to specify more clearly which noun is referred to in a given CONTEXT, such as blue in the PHRASE blue car.
An ADJECTIVE that is a MODIFIER of a NOUN, such as blue in the PHRASE blue car.

